南宁网站制作网络公司/seo建站优化推广
文章目录
- 一、补充
- 二、File类
- File类的含义
- 创建多级文件
- File类的常见方法
- 三、IO流
- IO流分类
- 输入输出流
- FileOutputStream
- InputStream
- InputStream与OutputStream的实例
- Reader
- Writer
- FileReader和FileWriter的实例
- 缓冲流
- 转换流
- 序列化与ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
- 打印流
- Properties
参考文章:Java IO流(超详细)
参考文章:文件操作
参考文章:最全最详细的IO流教程
一、补充
1. 文件分隔符小知识
- Windows:D:\Soft\QQ\Plugin
- Linux:D:/Soft/QQ/Plugin
2. 换行
- Windows:换行 = 回车+换行,即\r\n
- Linux:换行 = 换行,即\n
3. IDEA默认的当前路径
- 工程Project的根就是IDEA的默认当前路径
4. IDEA文件分隔符格式
- Windows: File file = new File(D:\test\test.txt);
- Linux:File file = new File(D://test//test.txt);
- 统一:File testFile = new File(“D:” + File.separator + “test” + File.separator + fileName);
二、File类
File类的含义
- File(String path):如果 path 是实际存在的路径,则该 File 对象表示的是目录;如果 path 是文件名,则该 File 对象表示的是文件。
创建多级文件
例如:D:\filepath\test\test.txt,先创建多级目录D:\filepath\test,在创建文件test.txt
package com.zte.FileTest;import sun.net.ftp.FtpClient;
//import com.zte.ums.cnms.pm.load.enums.MppFileDirEnum;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;public class FileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File testFile = new File("D:" + File.separator + "filepath" + File.separator + "test" + File.separator + "test.txt");File fileParent = testFile.getParentFile();//返回的是File类型,可以调用exsit()等方法 System.out.println("fileParent:" + fileParent);if (!fileParent.exists()) {fileParent.mkdirs();// 能创建多级目录}if (!testFile.exists())testFile.createNewFile();//有路径才能创建文件System.out.println(testFile);String path = testFile.getPath();String absolutePath = testFile.getAbsolutePath();String getFileName = testFile.getName();System.out.println("path:"+path);System.out.println("absolutePath:"+absolutePath);System.out.println("getFileName:"+getFileName);}
}输出结果:
fileParent:D:\filepath\test
D:\filepath\test\test.txt
path:D:\filepath\test\test.txt
absolutePath:D:\filepath\test\test.txt
getFileName:test.txt
File类的常见方法
public class FileGet {public static void main(String[] args) {File f = new File("d:/aaa/bbb.java"); //文件绝对路径:d:\aaa\bbb.java System.out.println("文件绝对路径:"+f.getAbsolutePath());//文件构造路径:d:\aaa\bbb.javaSystem.out.println("文件构造路径:"+f.getPath());//文件名称:bbb.javaSystem.out.println("文件名称:"+f.getName());//文件长度:2116字节System.out.println("文件长度:"+f.length()+"字节");//是否存在:trueSystem.out.println(f.exists());}
}
三、IO流
IO流分类
1. 字节流
按照 字节 的方式读取数据,一次读取1个字节byte,等同于一次读取8个二进制位。
这种流是万能的,什么类型的文件都可以读取。包括:文本文件,图片,声音文件,视频文件 等
eg.
假设文件file1.txt,采用字节流的话是这样读的:
a中国bc张三fe
第一次读:一个字节,正好读到’a’
第二次读:一个字节,正好读到’中’字符的一半。
第三次读:一个字节,正好读到’中’字符的另外一半。
2. 字符流
按照 字符 的方式读取数据的,一次读取一个字符.
这种流是为了方便读取 普通文本文件 而存在的,这种流不能读取:图片、声音、视频等文件。只能读取 纯文本文件,连word文件都无法读取。
注意:
纯文本文件,不单单是.txt文件,还包括 .java、.ini、.py 。总之只要 能用记事本打开 的文件都是普通文本文件。
3. 字符流和字节流的爱恨情仇
- 字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表
输入输出流
FileOutputStream
1. 构造方法
- public FileOutputStream(File file):以File对象为参数创建对象
- public FileOutputStream(String name):根据文件名称创建对象
// 使用File对象创建流对象
File file = new File("G:\\自动创建的文件夹\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("G:\\b.txt");
2. 实现数据追加
每次程序运行,每次创建输出流对象,都会清空目标文件中的数据。如何保留目标文件中数据,还能继续追加新数据呢?并且实现换行呢?其实很简单,这个时候我们又要再学习FileOutputStream的另外两个构造方法
- public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
- public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt",true); // 字符串转换为字节数组byte[] b = "abcde".getBytes();// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是c,两个字节,也就是cd。fos.write(b);// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
文件操作前:cd
文件操作后:cdabcde
3. 输出数据
写出指定字节
public void write(int b)
public void write(byte[] b)
public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) //从`off`索引开始,`len`个字节
写出字节:write(int b) 方法,每次可以写出一个字节数据,代码如下:
public class IoWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt"); // 写出数据fos.write(97); // 写出第1个字节fos.write(98); // 写出第2个字节fos.write(99); // 写出第3个字节// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
输出结果:
abc
写出数组
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt"); // 字符串转换为字节数组byte[] b = "麻麻我想吃烤山药".getBytes();// 写出字节数组数据fos.write(b);// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
输出结果:
麻麻我想吃烤山药
写出数组指定部分
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt"); // 字符串转换为字节数组byte[] b = "abcde".getBytes();// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是c,两个字节,也就是cd。fos.write(b,2,2);// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
输出结果:
cd
InputStream
1. 构造方法
- public FileInputStream(File file):以File对象为参数创建对象
- public FileInputStream(String name):根据文件名称创建对象
// 使用File对象创建流对象
File file = new File("G:\\自动创建的文件夹\\a.txt");
FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream(file);// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream("G:\\b.txt");
2. 读取字节数据
read方法,每次可以读取一个字节的数据,提升为int类型,读取到文件末尾,返回-1。
代码测试如下【read.txt文件中内容为abcde】
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");//read.txt文件中内容为abcde// 读取数据,返回一个字节int read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);// 读取到末尾,返回-1read = fis.read();System.out.println( read);// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}
输出结果:
a
b
c
d
e
-1
循环读取
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");// 定义变量,保存数据int b ;// 循环读取while ((b = fis.read())!=-1) {System.out.println((char)b);}// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}
输出结果:
a
b
c
d
e
3. 错误读取
read(byte[] b),每次读取b的长度个字节到数组中,返回读取到的有效字节个数,读取到末尾时,返回-1
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象.FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt"); // read.txt文件中内容为abcde// 定义变量,作为有效个数int len ;// 定义字节数组,作为装字节数据的容器 byte[] b = new byte[2];// 循环读取while (( len= fis.read(b))!=-1) {// 每次读取后,把数组变成字符串打印System.out.println(new String(b));}// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}输出结果:
ab
cd
ed
由于read.txt文件中内容为abcde,而错误数据d,是由于最后一次读取时,只读取一个字节e,数组中,上次读取的数据没有被完全替换【注意是替换,看下图】,所以要通过len ,获取有效的字节
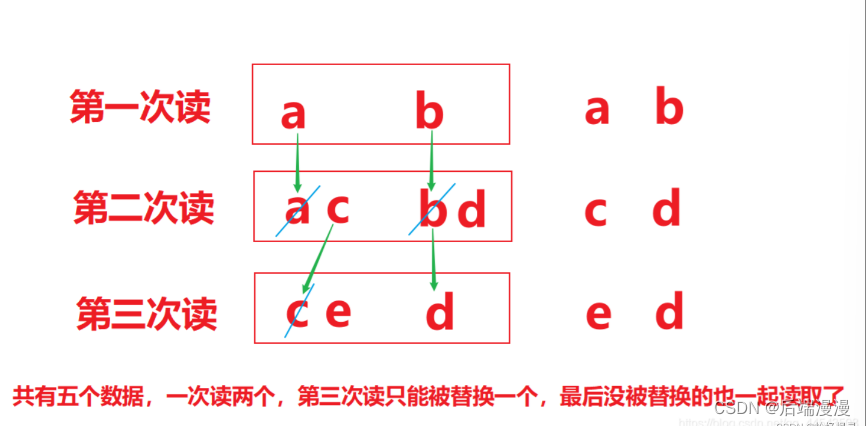
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象.FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt"); // 文件中为abcde// 定义变量,作为有效个数int len ;// 定义字节数组,作为装字节数据的容器 byte[] b = new byte[2];// 循环读取while (( len= fis.read(b))!=-1) {// 每次读取后,把数组的有效字节部分,变成字符串打印System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));// len 每次读取的有效字节个数}// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}输出结果:
ab
cd
e
InputStream与OutputStream的实例
public class Copy {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1.创建流对象// 1.1 指定数据源FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.jpg");// 1.2 指定目的地FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test_copy.jpg");// 2.读写数据// 2.1 定义数组byte[] b = new byte[1024];// 2.2 定义长度int len;// 2.3 循环读取while ((len = fis.read(b))!=-1) {// 2.4 写出数据fos.write(b, 0 , len);}// 3.关闭资源fos.close();fis.close();}
}Reader
1. 构造方法
- public FileReader(File file):以File对象为参数创建对象
- public FileReader(String name):根据文件名称创建对象
// 使用File对象创建流对象
File file = new File("G:\\自动创建的文件夹\\a.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream("G:\\b.txt");
2. 读取字符
read方法,每次可以读取一个字符的数据,提升为int类型,读取到文件末尾,返回-1
public class FRRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");// 定义变量,保存数据int b ;// 循环读取while ((b = fr.read())!=-1) {System.out.println((char)b);}// 关闭资源fr.close();}
}
Writer
1. 构造方法
- public FileWriter(File file):以File对象为参数创建对象
- public FileWriter(String name):根据文件名称创建对象
public class FileWriterConstructor {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 第一种:使用File对象创建流对象File file = new File("a.txt");FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);// 第二种:使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");}
}
2. 续写和换行
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象,可以续写数据FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt",true); // 写出字符串fw.write("哥敢");// 写出换行fw.write("\r\n");// 写出字符串fw.write("摸屎");// 关闭资源fw.close();}
}
输出结果:
哥敢
摸屎
3. 写出数据
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt"); // 写出数据fw.write(97); // 写出第1个字符fw.write('b'); // 写出第2个字符fw.write('C'); // 写出第3个字符//关闭资源时,与FileOutputStream不同。 如果不关闭,数据只是保存到缓冲区,并未保存到文件。// fw.close();}
}
输出结果:
abC
4. 关闭close与刷新flush
- flush :刷新缓冲区,流对象可以继续使用。
- close:先刷新缓冲区,然后通知系统释放资源。流对象不可以再被使用了。
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");// 写出数据,通过flushfw.write('刷'); // 写出第1个字符fw.flush();fw.write('新'); // 继续写出第2个字符,写出成功fw.flush();// 写出数据,通过closefw.write('关'); // 写出第1个字符fw.close();fw.write('闭'); // 继续写出第2个字符,【报错】java.io.IOException: Stream closedfw.close();}
}
FileReader和FileWriter的实例
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;public class CopyFile {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建输入流对象FileReader fr=new FileReader("F:\\新建文件夹\\aa.txt");//文件不存在会抛出java.io.FileNotFoundException//创建输出流对象FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("C:\\copyaa.txt");/*创建输出流做的工作:* 1、调用系统资源创建了一个文件* 2、创建输出流对象* 3、把输出流对象指向文件 * *///文本文件复制,一次读一个字符copyMethod1(fr, fw);//文本文件复制,一次读一个字符数组copyMethod2(fr, fw);fr.close();fw.close();}public static void copyMethod1(FileReader fr, FileWriter fw) throws IOException {int ch;while((ch=fr.read())!=-1) {//读数据fw.write(ch);//写数据}fw.flush();}public static void copyMethod2(FileReader fr, FileWriter fw) throws IOException {char chs[]=new char[1024];int len=0;while((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1) {//读数据fw.write(chs,0,len);//写数据}fw.flush();}
}CopyFile
缓冲流
1. 缓冲流的基本原理
-
- 使用了底层流对象从具体设备上获取数据,并将数据存储到缓冲区的数组内。
-
- 通过缓冲区的read()方法从缓冲区获取具体的字符数据,这样就提高了效率。
-
- 如果用read方法读取字符数据,并存储到另一个容器中,直到读取到了换行符时,将另一个容器临时存储的数据转成字符串返回,就形成了readLine()功能。
也就是说在创建流对象时,会创建一个内置的默认大小的缓冲区数组,通过缓冲区读写,减少系统IO次数,从而提高读写的效率。
2. 缓冲流的分类
- 字节缓冲流:BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream
- 字符缓冲流:BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
3. 示例
//1. 创建字节缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("b.txt"));//2. 创建字节缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("b.txt"));//3. 创建字符缓冲输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("b.txt"));//4. 创建字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt"));
转换流
1. InputStreamReader类-----(字节流到字符流的桥梁)
转换流java.io.InputStreamReader,是Reader的子类,从字面意思可以看出它是从字节流到字符流的桥梁。它读取字节,并使用指定的字符集将其解码为字符。
构造方法
- InputStreamReader(InputStream in): 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。
- InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName): 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("in.txt"));
InputStreamReader isr2 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("in.txt") , "GBK");
2. OutputStreamWriter类-----(字符流到字节流的桥梁)
字面看容易混淆会误以为是转为字符流,其实不然,OutputStreamWriter为从字符流到字节流的桥梁。使用指定的字符集将字符编码为字节。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集。
序列化与ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
1. 何谓序列化
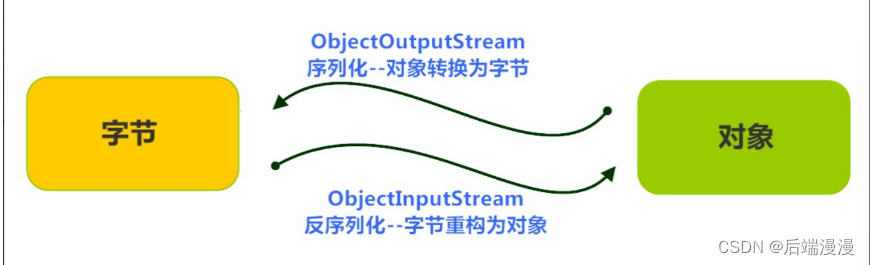
Java 提供了一种对象序列化的机制。用一个字节序列可以表示一个对象,该字节序列包含该对象的数据、对象的类型和对象中存储的属性等信息。字节序列写出到文件之后,相当于文件中持久保存了一个对象的信息。
反之,该字节序列还可以从文件中读取回来,重构对象,对它进行反序列化。对象的数据、对象的类型和对象中存储的数据信息,都可以用来在内存中创建对象。看图理解序列化
2. 序列化和反序列化的两个类
- ObjectOutputStream 类,将Java对象的原始数据类型写出到文件,实现对象的持久存储。
- ObjectInputStream类,将之前使用ObjectOutputStream序列化的原始数据恢复为对象。
创建可序列化对象,必须满足两个条件:
- 该类必须实现java.io.Serializable 接口,Serializable 是一个标记接口,不实现此接口的类将不会使任何状态序列化或反序列化,会抛出NotSerializableException 。
- 该类的所有属性必须是可序列化的。如果有一个属性不需要可序列化的,则该属性必须注明是瞬态的,使用transient 关键字修饰。
public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable {public String name;public String address;public transient int age; // transient瞬态修饰成员,不会被序列化public void addressCheck() {System.out.println("Address check : " + name + " -- " + address);}
}
序列化对象
public final void writeObject (Object obj) : 将指定的对象写出。public class SerializeDemo{public static void main(String [] args) {Employee e = new Employee();e.name = "zhangsan";e.address = "beiqinglu";e.age = 20; try {// 创建序列化流对象ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("employee.txt"));// 写出对象out.writeObject(e);// 释放资源out.close();fileOut.close();System.out.println("Serialized data is saved"); // 姓名,地址被序列化,年龄没有被序列化。} catch(IOException i) {i.printStackTrace();}}
}
输出结果:
Serialized data is saved
反序列化创建对象
public final Object readObject () : 读取一个对象。
public class DeserializeDemo {public static void main(String [] args) {Employee e = null;try { // 创建反序列化流FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("employee.txt");ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn);// 读取一个对象e = (Employee) in.readObject();// 释放资源in.close();fileIn.close();}catch(IOException i) {// 捕获其他异常i.printStackTrace();return;}catch(ClassNotFoundException c) {// 捕获类找不到异常System.out.println("Employee class not found");c.printStackTrace();return;}// 无异常,直接打印输出System.out.println("Name: " + e.name); // zhangsanSystem.out.println("Address: " + e.address); // beiqingluSystem.out.println("age: " + e.age); // 0}
}
打印流
1. 分类
字节打印流PrintStream,字符打印流PrintWriter
2. 示例
PrintStream复制文本文件
public class PrintStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("copy.txt"));PrintStream ps=new PrintStream("printcopy.txt");String line;while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {ps.println(line);}br.close();ps.close();}
}
PrintWriter复制文本文件
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
/*** 使用打印流复制文本文件*/
public class PrintWriterDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("aa.txt"));PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter("printcopyaa.txt");String line;while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {pw.println(line);}br.close();pw.close();}
}
Properties
我想各位对这个Properties类多多少少也接触过了,首先Properties类并不在IO包下,那为啥要和IO流一起讲呢?原因很简单因为properties类经常和io流的联合一起使用。
1. 特有功能
- public Object setProperty(String key,String value)
- public String getProperty(String key)
- public Set stringPropertyNames()
public class ProDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {// 创建属性集对象Properties properties = new Properties();// 添加键值对元素properties.setProperty("filename", "a.txt");properties.setProperty("length", "209385038");properties.setProperty("location", "D:\\a.txt");// 打印属性集对象System.out.println(properties);// 通过键,获取属性值System.out.println(properties.getProperty("filename"));System.out.println(properties.getProperty("length"));System.out.println(properties.getProperty("location"));// 遍历属性集,获取所有键的集合Set<String> strings = properties.stringPropertyNames();// 打印键值对for (String key : strings ) {System.out.println(key+" -- "+properties.getProperty(key));}}
}
输出结果:
{filename=a.txt, length=209385038, location=D:\a.txt}
a.txt
209385038
D:\a.txt
filename -- a.txt
length -- 209385038
location -- D:\a.txt2. IO流结合
把键值对形式的文本文件内容加载到集合中
public void load(Reader reader)
public void load(InputStream inStream)
3. 把集合中的数据存储到文本文件中
public void store(Writer writer,String comments)
public void store(OutputStream out,String comments)
public class ProDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {// 创建属性集对象Properties pro = new Properties();// 加载文本中信息到属性集pro.load(new FileInputStream("Properties.txt"));// 遍历集合并打印Set<String> strings = pro.stringPropertyNames();for (String key : strings ) {System.out.println(key+" -- "+pro.getProperty(key));}}
}
输出结果:
filename -- Properties.txt
length -- 123
location -- C:\Properties.txt